01
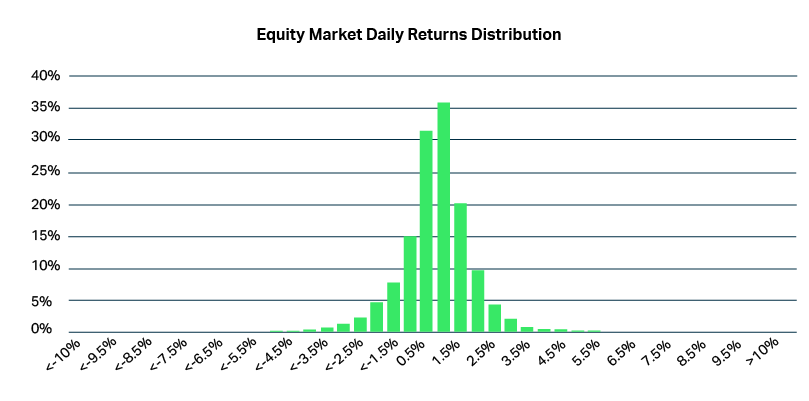
Structured products provide investors with a pre-determined risk/return profile
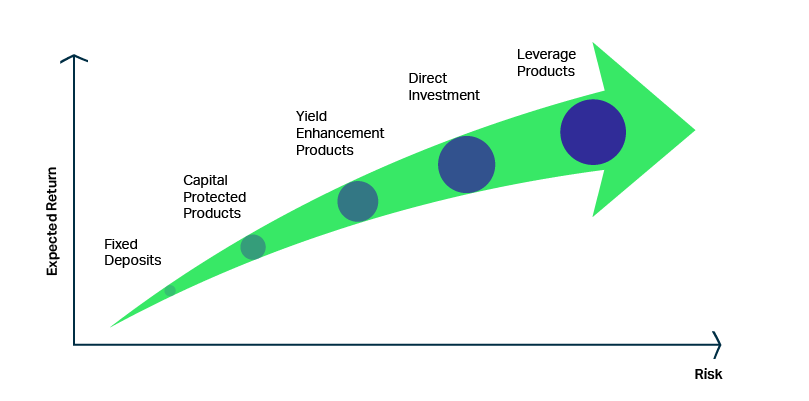
Investing in Structured Products offers unique risk-return opportunities distinct from traditional assets. This introduction explores the fundamentals of these intricate financial instruments.

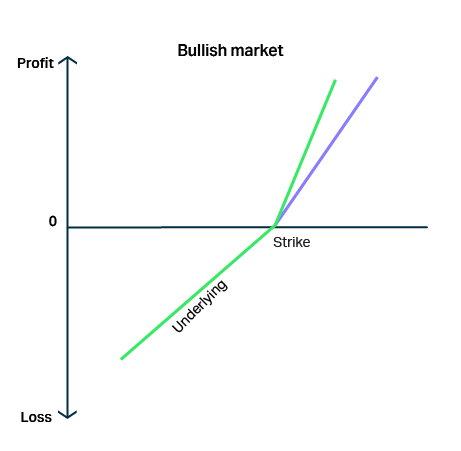
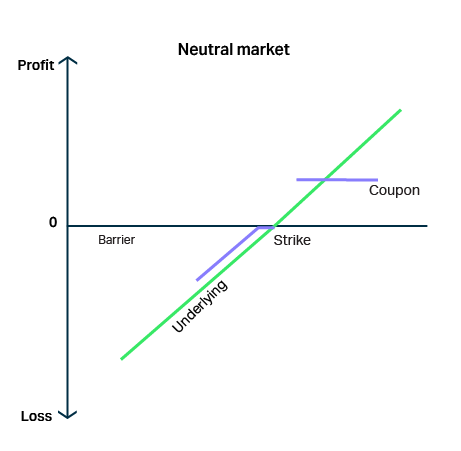
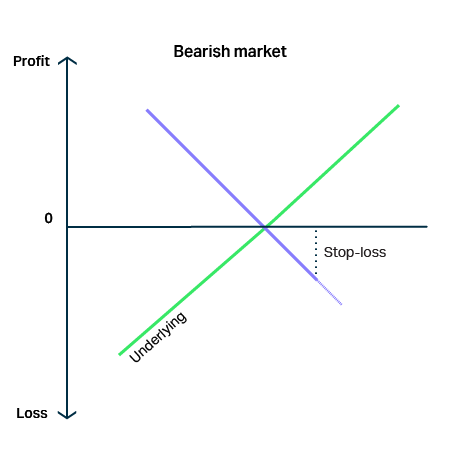
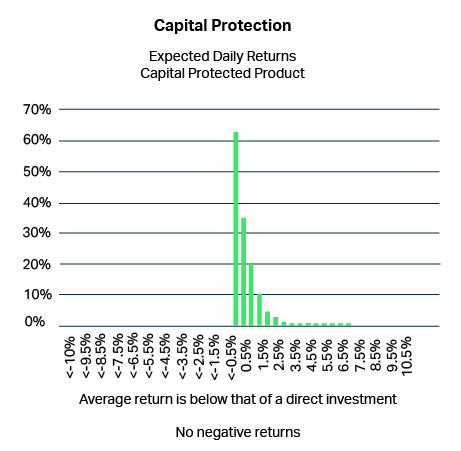
Capital protection
Structured products typically offer some form of capital protection. Depending on the investor’s preferences, structured investments are available to completely minimise risk exposure.
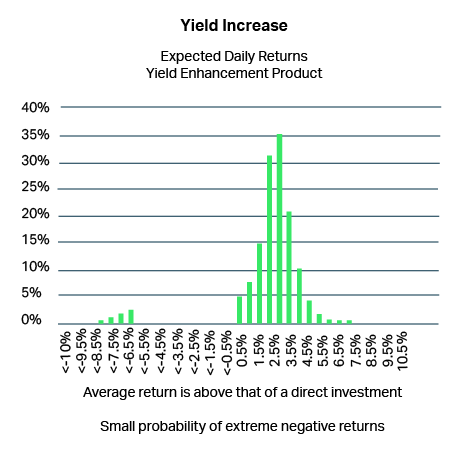
Yield enhancement
Structured products can offer a higher yield on sideways markets.
Market access
Investors can easily gain access to a new market or asset class that wasn't available through domestic securities.
Exchange risk management
Buying structured products or structured notes denominated in the portfolio currency can reduce exchange risk.
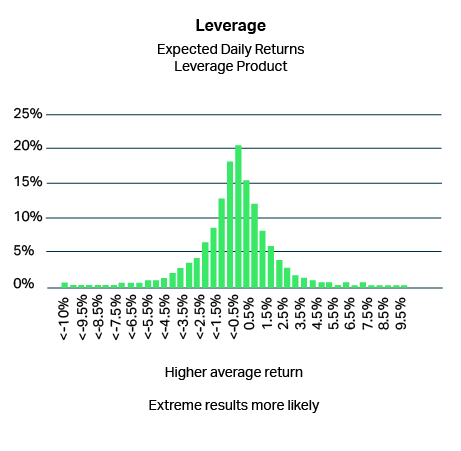
Leverage
Structured products can give leveraged exposure to markets.
Shorting/range trades
Investors benefit from falling or range-bound markets.
Market risk
The return from the investment is zero or even negative due to adverse market conditions. Investment advice on future market trends is needed to ensure the payoff is understood and reflects that view.
Counterparty risk
The investment issuer does not repay the principal or return. An assessment of the issuer’s credit rating and of any other relevant information (credit default spreads, balance sheet strength...) are needed.
Liquidity risk
There is only one market maker for the investment who does not provide an after-sales market or quotes a wide bid-offer spread. There are only buy-only investments where the issuer commits to making a competitive aftersales market in a place that is visible to the investor or their adviser.
Credit risk
If the asset goes bankrupt, for example, the bond issuer within a portfolio does not repay the principal. Investors should assess the creditworthiness of the assets the solution is linked to (if disclosed) and their credit ratings.
Launched in 2003, SRP is the leading provider of intelligence for the global structured product market, trusted by investment banks, hedge funds, product issuers and distributors, exchanges and asset managers.
Today, we enable market players to find any product from over 40 million in our database and easily analyse the market. Our news service and global events cover the latest insights into the structured products market and recognises industry leading talent through our awards programmes.
Learn more